云原生的工作流引擎 argo 试玩

Argo Workflows是一个开源的容器本机工作流引擎,用于在Kubernetes上协调并行作业。 Argo Workflows被实现为Kubernetes CRD(自定义资源定义)。跟其他传统的工作流引擎不同的是,他的每一个步骤都是一个容器。将多步骤工作流建模为一系列任务,或者使用有向无环图(DAG)捕获任务之间的依赖关系。
使用Kubernetes上的Argo Workflow,可以在短时间内轻松运行用于计算机学习或数据处理的计算密集型作业。
安装argo
安装argo十分容易
第一步先创建namespace
kubectl create ns argo
第二步执行 kubectl -n argo apply -f install.yaml
# This is an auto-generated file. DO NOT EDIT
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: clusterworkflowtemplates.argoproj.io
spec:
group: argoproj.io
names:
kind: ClusterWorkflowTemplate
listKind: ClusterWorkflowTemplateList
plural: clusterworkflowtemplates
shortNames:
- clusterwftmpl
- cwft
singular: clusterworkflowtemplate
scope: Cluster
version: v1alpha1
versions:
- name: v1alpha1
served: true
storage: true
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: cronworkflows.argoproj.io
spec:
group: argoproj.io
names:
kind: CronWorkflow
listKind: CronWorkflowList
plural: cronworkflows
shortNames:
- cwf
- cronwf
singular: cronworkflow
scope: Namespaced
version: v1alpha1
versions:
- name: v1alpha1
served: true
storage: true
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: workfloweventbindings.argoproj.io
spec:
group: argoproj.io
names:
kind: WorkflowEventBinding
listKind: WorkflowEventBindingList
plural: workfloweventbindings
shortNames:
- wfeb
singular: workfloweventbinding
scope: Namespaced
version: v1alpha1
versions:
- name: v1alpha1
served: true
storage: true
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: workflows.argoproj.io
spec:
additionalPrinterColumns:
- JSONPath: .status.phase
description: Status of the workflow
name: Status
type: string
- JSONPath: .status.startedAt
description: When the workflow was started
format: date-time
name: Age
type: date
group: argoproj.io
names:
kind: Workflow
listKind: WorkflowList
plural: workflows
shortNames:
- wf
singular: workflow
scope: Namespaced
subresources: {}
version: v1alpha1
versions:
- name: v1alpha1
served: true
storage: true
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: workflowtemplates.argoproj.io
spec:
group: argoproj.io
names:
kind: WorkflowTemplate
listKind: WorkflowTemplateList
plural: workflowtemplates
shortNames:
- wftmpl
singular: workflowtemplate
scope: Namespaced
version: v1alpha1
versions:
- name: v1alpha1
served: true
storage: true
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: argo
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: argo-server
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: argo-role
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- secrets
verbs:
- get
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
labels:
rbac.authorization.k8s.io/aggregate-to-admin: "true"
name: argo-aggregate-to-admin
rules:
- apiGroups:
- argoproj.io
resources:
- workflows
- workflows/finalizers
- workflowtemplates
- workflowtemplates/finalizers
- cronworkflows
- cronworkflows/finalizers
- clusterworkflowtemplates
- clusterworkflowtemplates/finalizers
verbs:
- create
- delete
- deletecollection
- get
- list
- patch
- update
- watch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
labels:
rbac.authorization.k8s.io/aggregate-to-edit: "true"
name: argo-aggregate-to-edit
rules:
- apiGroups:
- argoproj.io
resources:
- workflows
- workflows/finalizers
- workflowtemplates
- workflowtemplates/finalizers
- cronworkflows
- cronworkflows/finalizers
- clusterworkflowtemplates
- clusterworkflowtemplates/finalizers
verbs:
- create
- delete
- deletecollection
- get
- list
- patch
- update
- watch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
labels:
rbac.authorization.k8s.io/aggregate-to-view: "true"
name: argo-aggregate-to-view
rules:
- apiGroups:
- argoproj.io
resources:
- workflows
- workflows/finalizers
- workflowtemplates
- workflowtemplates/finalizers
- cronworkflows
- cronworkflows/finalizers
- clusterworkflowtemplates
- clusterworkflowtemplates/finalizers
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: argo-cluster-role
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
- pods/exec
verbs:
- create
- get
- list
- watch
- update
- patch
- delete
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- configmaps
verbs:
- get
- watch
- list
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- persistentvolumeclaims
verbs:
- create
- delete
- apiGroups:
- argoproj.io
resources:
- workflows
- workflows/finalizers
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- update
- patch
- delete
- create
- apiGroups:
- argoproj.io
resources:
- workflowtemplates
- workflowtemplates/finalizers
- clusterworkflowtemplates
- clusterworkflowtemplates/finalizers
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- serviceaccounts
verbs:
- get
- list
- apiGroups:
- argoproj.io
resources:
- cronworkflows
- cronworkflows/finalizers
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- update
- patch
- delete
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- events
verbs:
- create
- patch
- apiGroups:
- policy
resources:
- poddisruptionbudgets
verbs:
- create
- get
- delete
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: argo-server-cluster-role
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- configmaps
verbs:
- get
- watch
- list
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- secrets
verbs:
- get
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
- pods/exec
- pods/log
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- delete
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- events
verbs:
- watch
- create
- patch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- secrets
- serviceaccounts
verbs:
- get
- apiGroups:
- argoproj.io
resources:
- workflows
- workfloweventbindings
- workflowtemplates
- cronworkflows
- clusterworkflowtemplates
verbs:
- create
- get
- list
- watch
- update
- patch
- delete
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: argo-binding
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: argo-role
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: argo
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: argo-binding
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: argo-cluster-role
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: argo
namespace: argo
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: argo-server-binding
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: argo-server-cluster-role
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: argo-server
namespace: argo
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: workflow-controller-configmap
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: argo-server
spec:
externalIPs: # 暴露Service到外部IP
- 192.168.1.146 # IP
ports:
- name: web
port: 2746
targetPort: 2746
selector:
app: argo-server
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: workflow-controller-metrics
spec:
ports:
- name: metrics
port: 9090
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 9090
selector:
app: workflow-controller
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: argo-server
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: argo-server
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: argo-server
spec:
containers:
- args:
- server
image: argoproj/argocli:v2.11.7
name: argo-server
ports:
- containerPort: 2746
name: web
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /
port: 2746
scheme: HTTP
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 20
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /tmp
name: tmp
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/os: linux
serviceAccountName: argo-server
volumes:
- emptyDir: {}
name: tmp
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: workflow-controller
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: workflow-controller
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: workflow-controller
spec:
containers:
- args:
- --configmap
- workflow-controller-configmap
- --executor-image
- argoproj/argoexec:v2.11.7
command:
- workflow-controller
image: argoproj/workflow-controller:v2.11.7
name: workflow-controller
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/os: linux
serviceAccountName: argo
第三步 安装 argo-cli
# Download the binary
curl -sLO https://github.com/argoproj/argo/releases/download/v2.11.7/argo-darwin-amd64.gz
# Unzip
gunzip argo-darwin-amd64.gz
# Make binary executable
chmod +x argo-darwin-amd64
# Move binary to path
mv ./argo-darwin-amd64 /usr/local/bin/argo
# Test installation
argo version
如出现已下输出则 argo-cli 安装成功 我安装的是老版本 不用担心 是向下兼容的
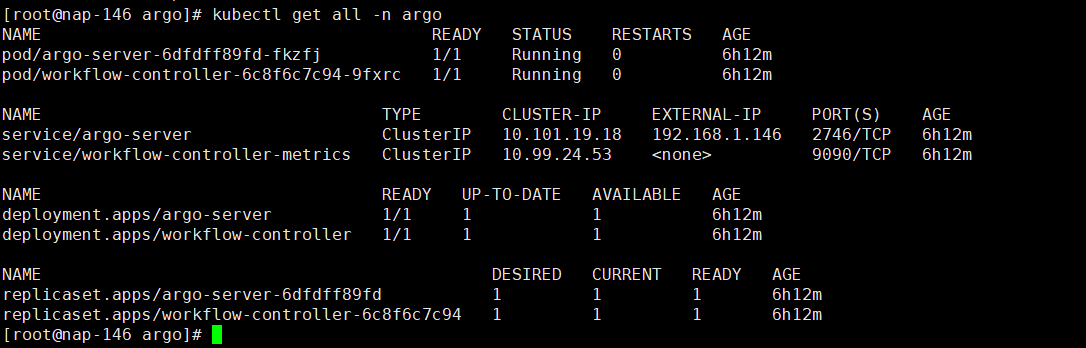
然后使用 kubectl get all -n argo查看argo-server的启动情况
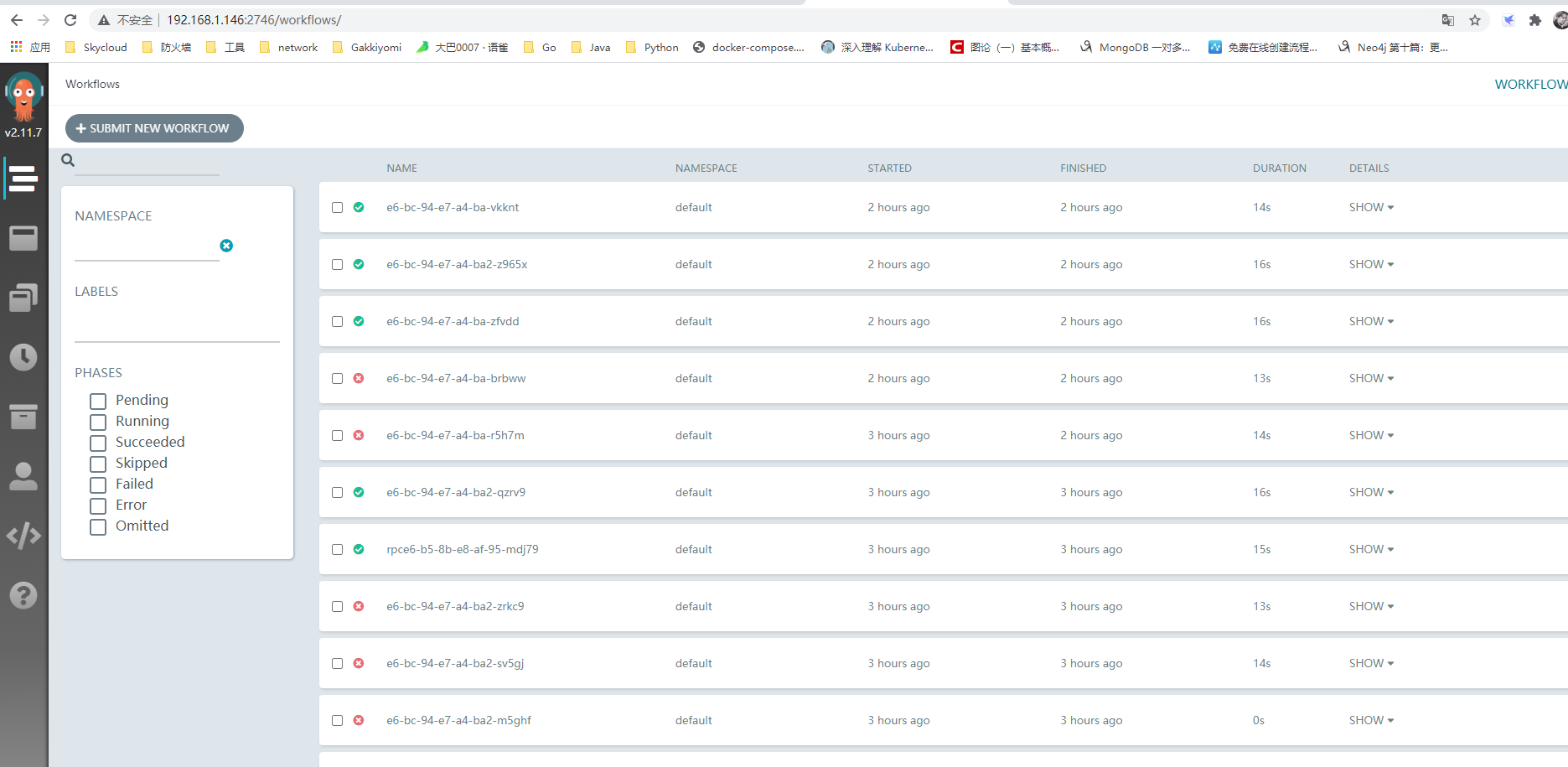
启动完毕后,我们可以访问暴露出来的argo-server-ui 界面访问argo-dashboard 默认端口2746
遇到的问题
安装完argo 并且提交工作流后,发现工作流执行不成功,查看日志发现
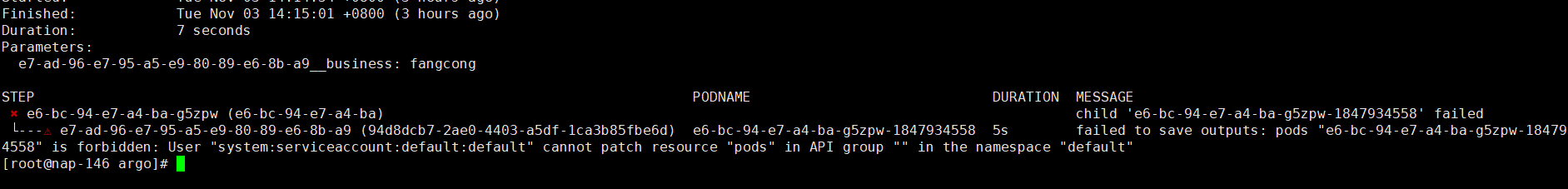
这是因为默认的工作流pod是在默认的namespace也就是default下执行的,而这个namespace下名为default的默认的serviceAccount不具备操作资源的权限,则我们可以给他绑定权限
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
namespace: default
name: pod-reader
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- configmaps
verbs:
- get
- watch
- list
- apiGroups:
- "batch"
resources:
- jobs
verbs:
- get
- watch
- list
- create
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- secrets
verbs:
- get
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
- pods/exec
- pods/log
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- delete
- patch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- events
verbs:
- watch
- create
- patch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- secrets
- serviceaccounts
verbs:
- get
- apiGroups:
- argoproj.io
resources:
- workflows
- workfloweventbindings
- workflowtemplates
- cronworkflows
- clusterworkflowtemplates
verbs:
- create
- get
- list
- watch
- update
- patch
- delete
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: pod-reader-pod
namespace: default
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: pod-reader
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: default
namespace: default
然后执行 kubectl apply -f role.yaml就可以解决这个问题
我们也可以在创建工作流的yaml指定我们创建好的有权限的serviceAccount
Hello World
我们可以使用官网的例子简单的开始第一个Workflow,一个Workflow基本也是这样的构造
- generateName: workflow会在k8s环境内产生一个job来执行workflow(job指的是k8s中一定会结束的任务),然后job则会产生以generateName规定的字符为前缀的pod(比如上面的例子,它会产生如whalesay-abcde字样的pod)
- entrypoint:这里规定了一个入口,即我们的workflow会以哪一个模板作为第一个模板来启动
- templates:定义了templates,templates是Argo中比较重要的一块,我们的Workflow运行都是基于各种template
argo-helloworld
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: whalesay-
spec:
entrypoint: whalesay
templates:
- name: whalesay # name of the template
container:
image: docker/whalesay
command: [cowsay]
args: ["hello world"]
以上是一个官网给出的helloworld样例。它规定了workflow会调用一个docker/whalesay的容器来打印helloworld。使用以下命令可以启动这个Workflow
argo submit helloworld.yaml
就可以看到workflow的启动,登录ui也可以看到此时有workflow的执行,打印helloworld
查看执行结果
使用 argo watch <workflowName> 持续监控工作流状态
使用argo logs <workflowName> 查看日志输出

步骤操作
步骤操作包含了比较多的模块类型,它提供了各种常见的对于步骤之间的操作,基本满足了我们对于步骤间操作的需求
container
这也是一个最常见的templates类型,它会创建一个容器,然后使用容器来完成我们的任务
- name: whalesay # name of the template
container:
image: docker/whalesay
command: [cowsay]
args: ["hello world"]
script
有时我们只希望我们的模板来运行一个脚本,那么Argo提供了Scripts来让我们运行脚本。
Script允许我们使用source标签来创建一个脚本(临时文件),然后这个临时文件的名称将会作为参数传递给command来执行。
使用script,会将运行脚本的标准输出分配给输出参数result,让其他的步骤来调用
针对不同的开发着,我们可以用不同的镜像来支持不同的执行方式
# shell脚本
- name: gen-random-int-bash
script:
image: debian:9.4
command: [bash]
source: | # Contents of the here-script
cat /dev/urandom | od -N2 -An -i | awk -v f=1 -v r=100 '{printf "%i\n", f + r * $1 / 65536}'
# python脚本
- name: gen-random-int-python
script:
image: python:alpine3.6
command: [python]
source: |
import random
i = random.randint(1, 100)
print(i)
# js脚本
- name: gen-random-int-javascript
script:
image: node:9.1-alpine
command: [node]
source: |
var rand = Math.floor(Math.random() * 100);
console.log(rand);
steps
steps规定了执行的步骤,有并行也有串行模式,它以双横杠(- -)的形式来定义串行,然后以单横杠的形式来定义并行
- name: hello-hello-hello
steps:
- - name: hello1 # hello1 is run before the following steps
template: whalesay
arguments:
parameters:
- name: message
value: "hello1"
- - name: hello2a # double dash => run after previous step
template: whalesay
arguments:
parameters:
- name: message
value: "hello2a"
- name: hello2b # single dash => run in parallel with previous step
template: whalesay
arguments:
parameters:
- name: message
value: "hello2b"
dag
DAG是一个有向无环图,Argo使用DAG来定义一些比较复杂的workflow关系
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: dag-diamond-
spec:
entrypoint: diamond
templates:
- name: echo
inputs:
parameters:
- name: message
container:
image: alpine:3.7
command: [echo, "{{inputs.parameters.message}}"]
- name: diamond
dag:
tasks:
- name: A
template: echo
arguments:
parameters: [{name: message, value: A}]
- name: B
dependencies: [A]
template: echo
arguments:
parameters: [{name: message, value: B}]
- name: C
dependencies: [A]
template: echo
arguments:
parameters: [{name: message, value: C}]
- name: D
dependencies: [B, C]
template: echo
arguments:
parameters: [{name: message, value: D}]
如上所示,上面的dag定义了一个钻石类型的图 A -> (B C) -> D
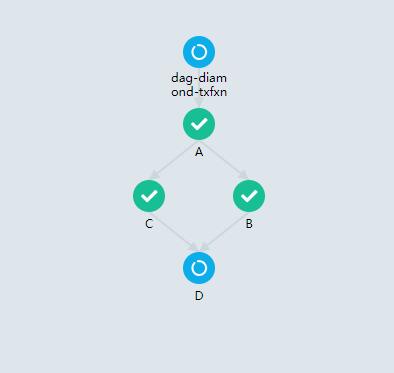
loop
使用loop我们可以定义循环
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: loops-
spec:
entrypoint: loop-example
templates:
- name: loop-example
steps:
- - name: print-message
template: whalesay
arguments:
parameters:
- name: message
value: "{{item}}"
withItems: # invoke whalesay once for each item in parallel
- hello world # item 1
- goodbye world # item 2
- name: whalesay
inputs:
parameters:
- name: message
container:
image: docker/whalesay:latest
command: [cowsay]
args: ["{{inputs.parameters.message}}"]
这个例子中,我们通过withItems传入了两个参数,然后Workflow就会并行执行这个templates两次,依次使用我们给出的参数
当然我们也可以动态的使用循环,循环的参数基于其他模板来控制
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: loops-param-result-
spec:
entrypoint: loop-param-result-example
templates:
- name: loop-param-result-example
steps:
- - name: generate
template: gen-number-list
# Iterate over the list of numbers generated by the generate step above
- - name: sleep
template: sleep-n-sec
arguments:
parameters:
- name: seconds
value: "{{item}}"
withParam: "{{steps.generate.outputs.result}}"
# Generate a list of numbers in JSON format
- name: gen-number-list
script:
image: python:alpine3.6
command: [python]
source: |
import json
import sys
json.dump([i for i in range(20, 31)], sys.stdout)
- name: sleep-n-sec
inputs:
parameters:
- name: seconds
container:
image: alpine:latest
command: [sh, -c]
args: ["echo sleeping for {{inputs.parameters.seconds}} seconds; sleep {{inputs.parameters.seconds}}; echo done"]
条件控制
条件的控制需要用到when的关键字
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: coinflip-
spec:
entrypoint: coinflip
templates:
- name: coinflip
steps:
# flip a coin
- - name: flip-coin
template: flip-coin
# evaluate the result in parallel
- - name: heads
template: heads # call heads template if "heads"
when: "{{steps.flip-coin.outputs.result}} == heads"
- name: tails
template: tails # call tails template if "tails"
when: "{{steps.flip-coin.outputs.result}} == tails"
# Return heads or tails based on a random number
- name: flip-coin
script:
image: python:alpine3.6
command: [python]
source: |
import random
result = "heads" if random.randint(0,1) == 0 else "tails"
print(result)
- name: heads
container:
image: alpine:3.6
command: [sh, -c]
args: ["echo \"it was heads\""]
- name: tails
container:
image: alpine:3.6
command: [sh, -c]
args: ["echo \"it was tails\""]
在这个例子中,Workflow通过when来判断第一步获取的值是head还是tails,根据获取的值来条件判断下一步会执行的步骤
重试
重试模块会定义如果Job执行出现failures或errors时的情况,
- limit:指重试的最大次数
- retryOn:指定重启策略
- Always: errors 和 failures时重启
- OnFailure: failures时重启,默认采用
- OnError: error时重启
- backoff:定义重启的一些参数
# This example demonstrates the use of retry back offs
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: retry-backoff-
spec:
entrypoint: retry-backoff
templates:
- name: retry-backoff
retryStrategy:
limit: 10
retryPolicy: "Always"
backoff:
duration: "1" # Must be a string. Default unit is seconds. Could also be a Duration, e.g.: "2m", "6h", "1d"
factor: 2
maxDuration: "1m" # Must be a string. Default unit is seconds. Could also be a Duration, e.g.: "2m", "6h", "1d"
container:
image: python:alpine3.6
command: ["python", -c]
# fail with a 66% probability
args: ["import random; import sys; exit_code = random.choice([0, 1, 1]); sys.exit(exit_code)"]
以上的例子定义了一个会重启的任务
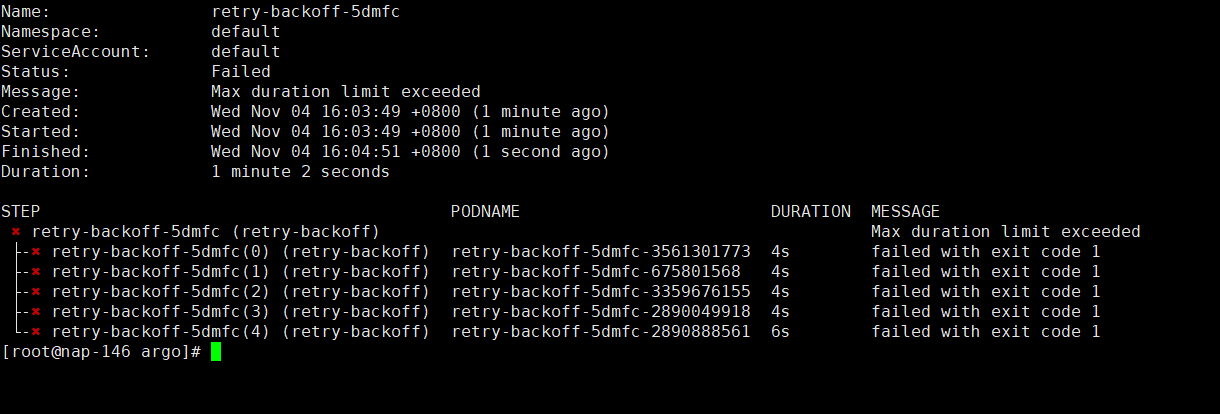
递归
argo 也是支持递归的,我们只要将步骤的下一步指定为本步骤即可
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: coinflip-recursive-
spec:
entrypoint: coinflip
templates:
- name: coinflip
steps:
# flip a coin
- - name: flip-coin
template: flip-coin
# evaluate the result in parallel
- - name: heads
template: heads # call heads template if "heads"
when: "{{steps.flip-coin.outputs.result}} == heads"
- name: tails # keep flipping coins if "tails"
template: coinflip
when: "{{steps.flip-coin.outputs.result}} == tails"
- name: flip-coin
script:
image: python:alpine3.6
command: [python]
source: |
import random
result = "heads" if random.randint(0,1) == 0 else "tails"
print(result)
- name: heads
container:
image: alpine:3.6
command: [sh, -c]
args: ["echo \"it was heads\""]
在以上的步骤中,step执行会做一个判断,如果一直是反面,会递归执行直到为正面

Exit handlers
Argo可以定义一个出口,它会直接退出工作流,无论成功与否。
常见于:
- 工作流运行后清理
- 发送工作流状态的通知(例如,电子邮件/ Slack)
- 将通过/失败状态发布到webhook结果(例如GitHub构建结果)
- 重新提交或提交另一个工作流程
spec:
entrypoint: intentional-fail
onExit: exit-handler # invoke exit-hander template at end of the workflow
templates:
- name: exit-handler
steps:
- - name: notify
template: send-email
- name: celebrate
template: celebrate
when: "{{workflow.status}} == Succeeded"
- name: cry
template: cry
when: "{{workflow.status}} != Succeeded"
在这里使用Onexit参数指定了结束模板,则执行exit-handler这个模板时,无论是否成功,都会直接结束
timeout
Argo定义了一个超时的限定,如果容器超时了,则直接结束Job
- name: sleep
container:
image: alpine:latest
command: [sh, -c]
args: ["echo sleeping for 1m; sleep 60; echo done"]
activeDeadlineSeconds: 10
suspending
- name: approve
suspend: {}
- name: delay
suspend:
duration: 20
如果我们使用了duration关键字,它会等待20秒后才唤醒执行
argo resume WORKFLOW # 这里的Workflow是指workflow的pod容器名
参数操作
参数传递对于工作流也是一个比较关键的问题。对于工作流来说,不同tempaltes之间的传递,是通过jinja来定义。目前Argo只接受以下几种前缀
- item
- steps
- inputs
- outputs
- workflow
- tasks
parameters
通常的参数传递是通过parameters关键字来定义的
- name: whalesay
inputs:
parameters:
- name: message # parameter declaration
container:
# run cowsay with that message input parameter as args
image: docker/whalesay
command: [cowsay]
args: ["{{inputs.parameters.message}}"]
arguments
我们可以通过arguments关键字来定义一个全局参数
entrypoint: whalesay
arguments:
parameters:
- name: message
value: hello world
- name: os-list # a list of items
value: |
[
{ "image": "debian", "tag": "9.1" },
{ "image": "debian", "tag": "8.9" },
{ "image": "alpine", "tag": "3.6" },
{ "image": "ubuntu", "tag": "17.10" }
]
在启动任务时,我们可以通过-p的参数来做实际参数,如果没有指定,则会使用默认参数(argument中定义)
argo submit arguments.yaml -p messgae="helloworld" -p oslist=[{ "image": "ubuntu", "tag": "17.10" }]
step间的传参
对于step间的传参,是通过step关键字来定义的
- name: test
steps:
- - name: A
template: A
- - name: B
template: B
when: "\"{{steps.A.outputs.result}}\" == \"B\""
- name: C
template: C
when: "\"{{steps.A.outputs.result}}\" == \"C\""
在以上例子中,定义了一个step,它会首先执行A步骤,然后根据启动结果,如果输出是B,则执行B步骤,否则执行C步骤
dag间的传参
对于Dag,其实它与step是十分相似的
dag:
tasks:
- name: ip
template: param
arguments:
parameters: [{name: request, value: "ip"}, {name: ip, value: "{{inputs.parameters.ip}}"}]
- name: port
template: param
arguments:
parameters: [{name: request, value: "port"}, {name: ip, value: "{{inputs.parameters.ip}}"}]
- name: username
template: param
arguments:
parameters: [{name: request, value: "username"}, {name: ip, value: "{{inputs.parameters.ip}}"}]
- name: password
template: param
arguments:
parameters: [{name: request, value: "password"}, {name: ip, value: "{{inputs.parameters.ip}}"}]
- name: server
template: server
dependencies: [ip, port, username, password]
arguments:
parameters:
- name: ip
value: "{{tasks.ip.outputs.result}}"
- name: password
value: "{{tasks.password.outputs.result}}"
- name: username
value: "{{tasks.username.outputs.result}}"
- name: port
value: "{{tasks.port.outputs.result}}"
在上面的例子中,dag并行执行(ip, port, username, password)四个步骤,然后将执行的结果传递给server模块,然后server模块会以这四个参数来完成工作。
script result
当我们运行一个script时,运行的标准输出会以result的方式来传递
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: scripts-bash-
spec:
entrypoint: bash-script-example
templates:
- name: bash-script-example
steps:
- - name: generate
template: gen-random-int-bash
- - name: print
template: print-message
arguments:
parameters:
- name: message
value: "{{steps.generate.outputs.result}}" # The result of the here-script
- name: gen-random-int-bash
script:
image: debian:9.4
command: [bash]
source: | # Contents of the here-script
cat /dev/urandom | od -N2 -An -i | awk -v f=1 -v r=100 '{printf "%i\n", f + r * $1 / 65536}'
- name: gen-random-int-python
script:
image: python:alpine3.6
command: [python]
source: |
import random
i = random.randint(1, 100)
print(i)
- name: gen-random-int-javascript
script:
image: node:9.1-alpine
command: [node]
source: |
var rand = Math.floor(Math.random() * 100);
console.log(rand);
- name: print-message
inputs:
parameters:
- name: message
container:
image: alpine:latest
command: [sh, -c]
args: ["echo result was: {{inputs.parameters.message}}"]
比如上面的例子,generate这个模块执行完成之后,print模块会获取generate模块的输出结果作为参数来执行
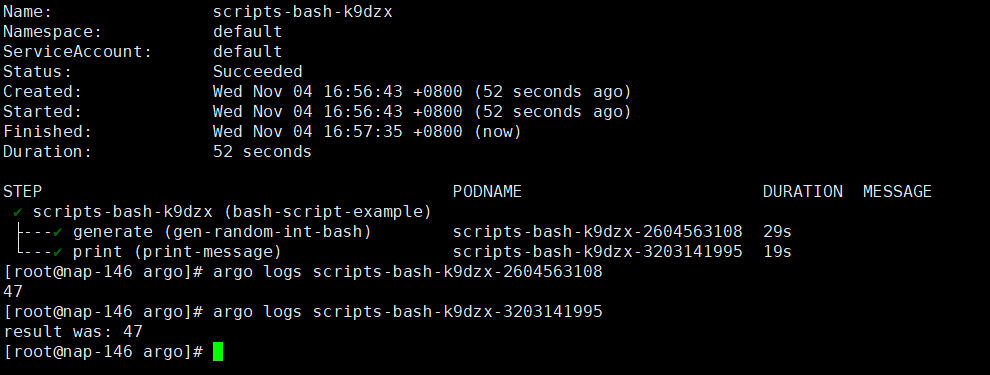
output Parameters
我们可以使用步骤的输出作为参数传递
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: output-parameter-
spec:
entrypoint: output-parameter
templates:
- name: output-parameter
steps:
- - name: generate-parameter
template: whalesay
- - name: consume-parameter
template: print-message
arguments:
parameters:
# Pass the hello-param output from the generate-parameter step as the message input to print-message
- name: message
value: "{{steps.generate-parameter.outputs.parameters.hello-param}}"
- name: whalesay
container:
image: docker/whalesay:latest
command: [sh, -c]
args: ["echo -n hello world > /tmp/hello_world.txt"] # generate the content of hello_world.txt
outputs:
parameters:
- name: hello-param # name of output parameter
valueFrom:
path: /tmp/hello_world.txt # set the value of hello-param to the contents of this hello-world.txt
- name: print-message
inputs:
parameters:
- name: message
container:
image: docker/whalesay:latest
command: [cowsay]
args: ["{{inputs.parameters.message}}"]
在上面的例子中,whalesay模块会将执行结果打印到hello-world.txt文本,然后将这个文本的内容定为输出结果然后consume-parameter模块会去获取whalesay模块的输出结果做为输入参数
资源操作
Argo可以操作的资源也有很多,它不仅仅是能操作容器,kubernetes的资源、容器资源、计算资源等也均可调配
Secret
volumes:
- name: my-secret-vol
secret:
secretName: my-secret # name of an existing k8s secret
templates:
- name: whalesay
container:
image: alpine:3.7
command: [sh, -c]
args: ['
echo "secret from env: $MYSECRETPASSWORD";
echo "secret from file: `cat /secret/mountpath/mypassword`"
']
env:
- name: MYSECRETPASSWORD # name of env var
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: my-secret # name of an existing k8s secret
key: mypassword # 'key' subcomponent of the secret
volumeMounts:
- name: my-secret-vol # mount file containing secret at /secret/mountpath
mountPath: "/secret/mountpath"
在这里,我们使用了Secret作为一个volume供模板调用
daemon
使用守护进程可以使得作业在后台运行,他们的存在使得有的工作可以跨工作流运行
- name: influxdb
daemon: true # start influxdb as a daemon
retryStrategy:
limit: 10 # retry container if it fails
container:
image: influxdb:1.2
readinessProbe: # wait for readinessProbe to succeed
httpGet:
path: /ping
port: 8086
在这里使用了daemon: true来开启daemon,以保护influxdb持续运行
sidecar
边车模式,指著容器在同一容器中同时执行另一个容器来支持主容器的工作。Argo也支持边车模式,可以启动一个辅助容器来协助作业的进行
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: sidecar-nginx-
spec:
entrypoint: sidecar-nginx-example
templates:
- name: sidecar-nginx-example
container:
image: appropriate/curl
command: [sh, -c]
# Try to read from nginx web server until it comes up
args: ["until `curl -G 'http://127.0.0.1/' >& /tmp/out`; do echo sleep && sleep 1; done && cat /tmp/out"]
# Create a simple nginx web server
sidecars:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.13
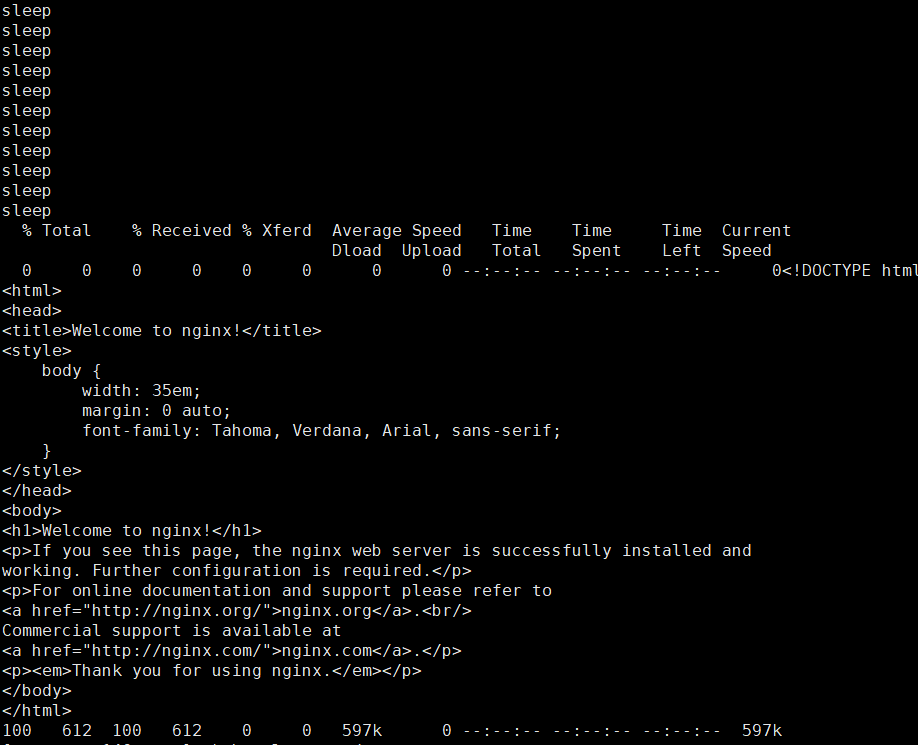
Artifacts
在Argo中也有集成一些比较常用的库,比如http和git
templates:
- name: hardwired-artifact
inputs:
artifacts:
# Check out the master branch of the argo repo and place it at /src
# revision can be anything that git checkout accepts: branch, commit, tag, etc.
- name: argo-source
path: /src
git:
repo: https://github.com/argoproj/argo.git
revision: "master"
# Download kubectl 1.8.0 and place it at /bin/kubectl
- name: kubectl
path: /bin/kubectl
mode: 0755
http:
url: https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/v1.8.0/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl
Resource
Argo可以操作k8s资源 创建一个job
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: k8s-jobs-
spec:
entrypoint: pi-tmpl
templates:
- name: pi-tmpl
resource: # indicates that this is a resource template
action: create # can be any kubectl action (e.g. create, delete, apply, patch)
successCondition: status.succeeded > 0
failureCondition: status.failed > 3
manifest: | #put your kubernetes spec here
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
generateName: pi-job-
spec:
template:
metadata:
name: pi
spec:
containers:
- name: pi
image: perl
command: ["perl", "-Mbignum=bpi", "-wle", "print bpi(2000)"]
restartPolicy: Never
backoffLimit: 4
可以使用以下Argo Workflow修改此Crontab:
apiVersion: "stable.example.com/v1"
kind: CronTab
spec:
cronSpec: "* * * * */5"
image: my-awesome-cron-image
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: k8s-patch-
spec:
entrypoint: cront-tmpl
templates:
- name: cront-tmpl
resource:
action: patch
mergeStrategy: merge # Must be one of [strategic merge json]
manifest: |
apiVersion: "stable.example.com/v1"
kind: CronTab
spec:
cronSpec: "* * * * */10"
image: my-awesome-cron-image
docker
Argo实现了Docker in Docker的形式
- name: dind-sidecar-example
container:
image: docker:17.10
command: [sh, -c]
args: ["until docker ps; do sleep 3; done; docker run --rm debian:latest cat /etc/os-release"]
env:
- name: DOCKER_HOST # the docker daemon can be access on the standard port on localhost
value: 127.0.0.1
sidecars:
- name: dind
image: docker:17.10-dind # Docker already provides an image for running a Docker daemon
securityContext:
privileged: true # the Docker daemon can only run in a privileged container
# mirrorVolumeMounts will mount the same volumes specified in the main container
# to the sidecar (including artifacts), at the same mountPaths. This enables
# dind daemon to (partially) see the same filesystem as the main container in
# order to use features such as docker volume binding.
mirrorVolumeMounts: true
以上工作流实现了主容器运行等待容器创建,边车容器启动一个容器并将这个容器镜像交给主容器资源
volumes
在Argo中,我们也可以直接传递容器卷,方便处理大量数据
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: volumes-pvc-
spec:
entrypoint: volumes-pvc-example
volumeClaimTemplates: # define volume, same syntax as k8s Pod spec
- metadata:
name: workdir # name of volume claim
spec:
accessModes: [ "ReadWriteOnce" ]
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi # Gi => 1024 * 1024 * 1024
templates:
- name: volumes-pvc-example
steps:
- - name: generate
template: whalesay
- - name: print
template: print-message
- name: whalesay
container:
image: docker/whalesay:latest
command: [sh, -c]
args: ["echo generating message in volume; cowsay hello world | tee /mnt/vol/hello_world.txt"]
# Mount workdir volume at /mnt/vol before invoking docker/whalesay
volumeMounts: # same syntax as k8s Pod spec
- name: workdir
mountPath: /mnt/vol
- name: print-message
container:
image: alpine:latest
command: [sh, -c]
args: ["echo getting message from volume; find /mnt/vol; cat /mnt/vol/hello_world.txt"]
# Mount workdir volume at /mnt/vol before invoking docker/whalesay
volumeMounts: # same syntax as k8s Pod spec
- name: workdir
mountPath: /mnt/vol
在上面的例子中,workflow初始化了一个容器卷,然后下面的whalesay和print-message模块都调用了这个容器卷
不过大多数情况下,我们会去调用一个已存在的卷
# Define Kubernetes PVC
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: my-existing-volume
spec:
accessModes: [ "ReadWriteOnce" ]
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
---
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: volumes-existing-
spec:
entrypoint: volumes-existing-example
volumes:
# Pass my-existing-volume as an argument to the volumes-existing-example template
# Same syntax as k8s Pod spec
- name: workdir
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: my-existing-volume
templates:
- name: volumes-existing-example
steps:
- - name: generate
template: whalesay
- - name: print
template: print-message
- name: whalesay
container:
image: docker/whalesay:latest
command: [sh, -c]
args: ["echo generating message in volume; cowsay hello world | tee /mnt/vol/hello_world.txt"]
volumeMounts:
- name: workdir
mountPath: /mnt/vol
- name: print-message
container:
image: alpine:latest
command: [sh, -c]
args: ["echo getting message from volume; find /mnt/vol; cat /mnt/vol/hello_world.txt"]
volumeMounts:
- name: workdir
mountPath: /mnt/vol
在上面的例子中,我们外部已经定义了一个pvc,然后在workflow中,我们通过声明一个pvc为卷来调用它
总结
argo是一个云原生的基于k8s的工作流引擎,如果基础环境是k8s的话,不管是ci/cd 还是其他工作流用途,argo都是非常好的选择,上手非常简单,使用yaml作为模板语法 与k8s几乎一模一样。
-
云原生
14 引用
-
Argo
1 引用
-
Kubernates
3 引用



辛苦了,我回去慢慢看,信息量有点大~
好贴!!在 cicd 有巨大的前景呀!
大佬令我难以望其项背